Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that affects millions of people. These veins typically appear as enlarged, twisted veins on the legs and are often associated with discomfort or swelling. Minimally invasive procedures performed by interventional radiologists may offer effective relief and a faster recovery compared to traditional surgical methods. Here is more information on interventional radiology (IR), the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for varicose veins, and how IR techniques assist in their management:
What Is Interventional Radiology?
Interventional radiology is a branch of medicine that uses imaging technologies, such as ultrasound, X-rays, and CT scans, to guide targeted, minimally invasive procedures. The goal of IR is to diagnose and treat medical conditions through tiny incisions or needle punctures, reducing the need for open surgery. These techniques are used for a variety of conditions, including vascular diseases, tumors, and organ dysfunction.
By relying on real-time imaging, interventional radiologists perform treatments with high precision. Advantages include reduced risk, less pain, fewer complications, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgical approaches. For varicose veins, IR techniques deliver focused treatment while avoiding large surgical wounds.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins occur when individual veins, typically in the legs, become enlarged and twisted. These veins have lost their ability to carry blood efficiently back to the heart, often due to weakened vein walls or faulty valves. Blood pooling in these veins leads to their distinct appearance and associated symptoms. Certain factors, like age, pregnancy, and occupation, may contribute to a higher risk of developing this condition.
What Causes Them?
The main cause of varicose veins is malfunctioning valves within the affected veins. Normally, these valves direct blood upwards toward the heart and prevent backward flow. When valves fail, blood accumulates in the veins, increasing pressure and causing them to stretch and dilate.
Genetics, pregnancy, obesity, prolonged standing or sitting, and previous blood clots can increase the likelihood of developing varicose veins. Family history is a frequent contributing factor. Occupations that require extended periods on one’s feet may also be connected with the condition.
What Are the Symptoms?
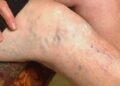
Varicose veins often present with visible bulging, rope-like veins beneath the skin. Common symptoms include aching pain, heaviness, swelling in the legs, and itching around the affected veins. Some patients may notice burning or throbbing sensations, especially after standing for long periods.
Complications may develop in advanced cases. This includes skin changes (discoloration or thickening), ulcer formation near the ankles, or superficial blood clots (phlebitis). Early intervention is suggested to prevent progression and reduce the risk of these complications.
How Are Varicose Veins Treated?
Treatment for varicose veins ranges from conservative measures to minimally invasive procedures. Initial approaches may include lifestyle changes, such as regular physical activity, weight management, leg elevation, and compression stockings. These strategies improve circulation and help manage symptoms but may not resolve the underlying problem.
Minimally invasive techniques are often used when conservative options do not provide sufficient relief. Here are some procedures interventional radiologists may suggest:
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Sclerotherapy
- Microphlebectomy
Treat Your Varicose Veins Today
Interventional radiology provides precise, minimally invasive options for the treatment of varicose veins, delivering effective symptom relief and improved appearance. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments helps patients make informed choices about management. If you are experiencing discomfort or visible changes from varicose veins, consult with a qualified interventional radiologist to discuss your options and determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Seek care early and take positive steps toward healthier legs.